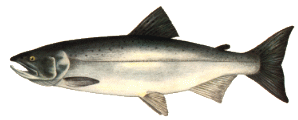
| COHO SALMON (also known as silver salmon, blue back) |
IDENTIFICATION & FEATURES: |
- Differs from chinook salmon by having white gums in a dark mouth
- Small black spots confined to the caudal fin and above the lateral line
- Silvery sides, steel grey back, white belly
|
|
HABITAT:
- Found in the Great Lakes at depths of 16 to 60m (49-197 ft.)
- Prefers water that is 12-14 C (53-57 F)
- Native of the West Coast
SPAWNING:
- At ages 3-4, moves into rivers in the fall to spawn
- Both males and females die after spawning
FOOD:
- Feeds on alewife, smelt, insects and crustaceans
ANGLING:
- In streams takes spinners, spawn and spawn imitations
- In lakes, may be caught by trolling spoons and salmon baits
|
|
| CHINOOK SALMON (also known as king salmon, pacific salmon) |
IDENTIFICATION & FEATURES: |
- Black spots on the head, back and both lobes of the caudal fin
- Mouth lining black with black gums
- Blue green head and back with silver sides
|

|
HABITAT:
- Found in the Great Lakes at depths of 16 to 60m (49-197 ft.)
- Prefers water that is 12-14 C (53-57 F)
- Native of the West Coast
SPAWNING:
- Usually spawns at age 4
- Moves into rivers in the fall to spawn
- Males and females die after spawning
FOOD:
- Feeds on alewife, smelt, insects and crustaceans
ANGLING:
- Caught in lakes by trolling spoons, plugs, dodgers and flies
- In streams in the fall, readily takes spawn and spinners
|
|
| PINK SALMON (also known as pink) |
IDENTIFICATION & FEATURES: |
- Large black spots on back and tail fin, but not on dorsal fin
- Bluish grey back, silvery sides and underparts
- Forked tail
- Narrow caudal peduncle
|

|
HABITAT:
- Introduced into Lake Superior in 1956 near Thunder Bay, this west coast salmon has spread naturally throughout the Great Lakes
SPAWNING:
- It travels up rivers in the fall to spawn
- At spawning time the males develop a humped back, hooked snout, dark back and red sides
- Males and females die after spawning
FOOD:
- Small fish, Smelt and insects
ANGLING:
- In streams takes spinners, spawn and spawn imitations
- In lakes, may be caught by trolling spoons and salmon baits
|
|
|







